PLEASE HELP ME!! WORTH 30 POINTS!!!
Drag the labels to the image. Each label can be used more than once.
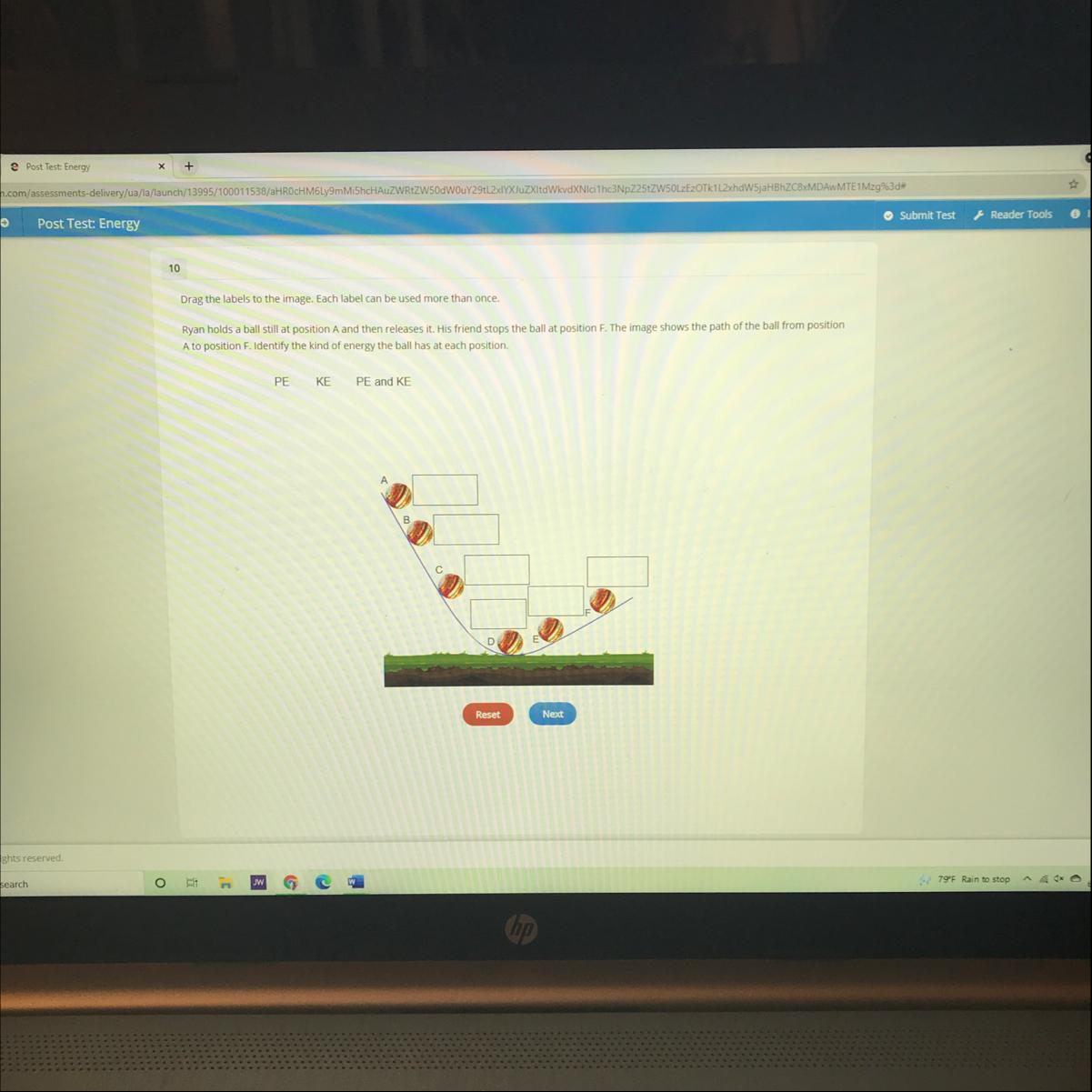
Ryan holds a ball still at position A and then releases it. His friend stops the ball at position F. The image shows the path of the ball from position A to position F. Identify the kind of energy the ball has at each position
PE
KE
PE and KE
Answers
The kind of energy the ball has at each position are A: PE,B: KE,C: KE,D: PE and KE,E: KE,F: PE.
What is the energy ?Energy is defined as the capacity for doing work. It is a fundamental concept in physics, and can take many forms, such as thermal, electrical, kinetic, potential, light, and sound energy. Energy is the ability to cause change, and it is present in all physical processes. All forms of energy can be converted into each other, and they are often interlinked in complex ways. For example, electricity can be created from light energy, and energy can be stored in batteries. In the natural world, energy is used to power physical and chemical processes, such as digestion, photosynthesis, and respiration.
To learn more about energy
https://brainly.com/question/19666326
#SPJ1
Related Questions
Neap tides happen when ?
Answers
which of the following can cause muscle fatigue ?
A.A build up of lactic acid
b.an inadequate supply of oxygen
C.an inadequate supply of glycogen
D.all of the above
Answers
Answer:
The correct answer is -all of the above.
Explanation:
Muscle fatigue is a reduced ability in work capacity caused by work itself. It is known that altering oxygen is contracting skeletal muscle affects performance. Reduced O2 supply increases the rate of muscle fatigue.
The lactic acid is accumulated as it forms rapidly but the breaking of the lactic acid is slow down, which causes muscle fatigue. Less ATP and glycogen in muscle results in fatigue as the muscle is not able to generate energy to power contractions and therefore contributes to muscle fatigue.
Hydrochloric acid is widely used as a laboratory reagent in refining ore for the production of tin and tantalum, and as a catalyst in organic reactions. Calculate the number of moles of HCl in 62.85 mL of 0.453 M hydrochloric acid.
Answers
Answer: 0.0285 moles of HCl is present in given amount of solution.
Explanation:
Molarity is defined as the amount of solute expressed in the number of moles present per liter of solution. The units of molarity are mol/L. The formula used to calculate molarity:
[tex]\text{Molarity of solution}=\frac{\text{Moles of solute}\times 1000}{\text{Volume of solution (mL)}}[/tex] .....(1)
Given values:
Molarity of HCl = 0.453 M
Volume of solution = 62.85 mL
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
[tex]0.453mol/L=\frac{\text{Moles of HCl}\times 1000}{62.85}\\\\\text{Moles of HCl}=\frac{0.453\times 62.85}{1000}=0.0285moles[/tex]
Hence, 0.0285 moles of HCl is present in given amount of solution.
Two experiments were conducted in a bomb calorimeter. The first one to determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter, the second the heat of combustion of the carcinogenic substance benzene (C6H6). a. In the first experiment, the temperature rises from 22.37 o C to 24.68 o C when the calorimeter absorbs 5682 J of heat. Determine the heat capacity of the calorimeter. Page 3 of 4 b. In the second experiment, the combustion of 0.258 g of benzene increases the temperature from 22.37 o C to 26.77 o C. Determine the heat of combustion for 1 mol of benzene.
Answers
Answer:
The right solution is:
(a) 2459.74 J/degree C
(b) 3271.769 KJ/moles
Explanation:
According to the question,
(a)
The heat capacity of the calorimeter will be:
= [tex]\frac{5682}{24.68-22.37}[/tex]
= [tex]\frac{5682}{2.31}[/tex]
= [tex]2459.74 \ J/degree \ C[/tex]
(b)
The change in temperature will be:
= [tex]26.77-22.37[/tex]
= [tex]4.4 \ Degree \ C[/tex]
The amount of heat released will be:
= [tex]2459.74\times 4.4[/tex]
= [tex]10822 \ Joules[/tex]
or,
= [tex]10.822 \ KJ[/tex]
Moles of benzene combusted will be:
= [tex]\frac{0.258}{78}[/tex]
= [tex]0.00330 \ Moles[/tex]
hence,
The heat combustion for 1 mol of benzene will be:
= [tex]\frac{10.822}{0.00330}[/tex]
= [tex]3271.769 \ KJ/moles[/tex]
What is 0.29km in mm
Answers
Explanation:
1 km=1,000,000 mm
0.29 km= 290,000 mm
Which one of the mixtures would most likely produce a chemical reaction?
F2 + At- OR At2 + F-
Answers
Answer:
F₂ + At⁻
Explanation:
Astatine is the only Halogen that does not exist as a diatomic molecule. One Astatine atom would have a charge of 1⁻. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, and therefore very reactive and commonly forms a diatomic molecule.
How many molecules are contained in 52.5 moles of C2H8?
please explain if you can
Answers
Answer:
3.1621 × 10²⁵ molecules
Explanation:
From the given information:
Moles of C2H8 = 52.5 moles
number of moles = mass/molar mass
molar mass of C2H8 = (6 *2) + (1*8)
= 12 + 8
= 20 g/mol
∴
52.5 moles = mass of C2H8 / 20 g/mol
mass of C2H8 = 52.5 moles × 20 g/mol
mass of C2H8 = 1050 grams
Recall that;
1 mole = 6.023 × 10²³ molecules
∴ 52.5 moles of C2H8 = (52.5 × 6.023 × 10²³) molecules
=3.1621 × 10²⁵ molecules
The solubility of a gas is 0.890 8/1 at a pressure of 121 kPa. What
is the solubility of the gas if the pressure is increased to 150 kPa,
given that the temperature is held constant?
Answers
Answer:
1.10 g/L
Explanation:
Step 1: Calculate Henry's constant (k)
The solubility of a gas (C) is 0.890 g/L at a pressure (P) of 121 kPa. Solubility and pressure are related through Henry's law.
C = k × P
k = C / P
k = (0.890 g/L) / 121 kPa = 7.36 × 10⁻³ g/L.kPa
Step 2: Calculate the solubility of the gas if the pressure is increased to 150 kPa
We will use Henry's law.
C = k × P
C = (7.36 × 10⁻³ g/L.kPa) × 150 kPa = 1.10 g/L
Solubility of the gas, if the temperature is held constant and pressure is increased to 150 kPa from 121 kPa, is 1.10 g/L.
What is Henry's law?Henry's law of gas states at solubility (C) of the dissolved gas is directly proportional to the partial pressure (P) of the gas.
C ∝ P
C = kP, where
k = Henry's constant
Let first we calculate the Henry's constant, when the solubility of a gas is 0.890 g/L at a pressure of 121 kPa is:
k = (0.890 g/L) / (121 kPa)
k = 7.36 × 10⁻³ g/L.kPa
Now we calculate the solubility of the gas, if the pressure is increased to 150 kPa as:
C = (7.36 × 10⁻³ g/L.kPa) (150 kPa)
C = 1.10 g/L
Hence, required solubility is 1.10 g/L.
To know more about Henry's constant, visit the below link:
https://brainly.com/question/7007748
A solution has a [H3O+] 1 x 10^-3 what is the [OH-] of the solution
Answers
Answer:
OH- is 1x 10^ + 3
Explanation:
- and - = +
At a certain temperature, 0.700 mol SO3 is placed in a 3.50 L container. 2SO3(g)↽−−⇀2SO2(g)+O2(g) At equilibrium, 0.180 mol O2 is present. Calculate c.
Answers
Answer: The value of [tex]K_c[/tex] for the given chemical equation is 0.0457.
Explanation:
Given values:
Initial moles of [tex]SO_3[/tex] = 0.700 moles
Volume of conatiner = 3.50 L
The given chemical equation follows:
[tex]2SO_3(g)\rightleftharpoons 2SO_2(g)+O_2(g)[/tex]
I: 0.700
C: -2x +2x x
E: 0.700-2x 2x x
Equilibrium moles of [tex]O_2[/tex] = x = 0.180 moles
Equilibrium moles of [tex]SO_2[/tex] = 2x = [tex](2\times 0.180)=0.360moles[/tex]
Equilibrium moles of [tex]SO_3[/tex] = 0.700 - 2x = [tex]0.700-(2\times 0.180)=0.340moles[/tex]
Molarity is calculated by using the equation:
[tex]Molarity=\frac{Moles}{Volume}[/tex]
So,
[tex][SO_3]_{eq}=\frac{0.340}{3.50}=0.0971M[/tex]
[tex][SO_2]_{eq}=\frac{0.360}{3.50}=0.103M[/tex]
[tex][O_2]_{eq}=\frac{0.180}{3.50}=0.0514M[/tex]
The expression of [tex]K_c[/tex] for above equation follows:
[tex]K_c=\frac{[SO_2]^2[O_2]}{[SO_3]^2}[/tex]
Plugging values in above expression:
[tex]K_c=\frac{(0.0971)^2\times 0.0514}{(0.103)^2}\\\\K_c=0.0457[/tex]
Hence, the value of [tex]K_c[/tex] for the given chemical equation is 0.0457.
An aqueous salt solution is 15.0% mass sodium chloride. How many grams of salt are in 250.0 grams of this solution? Use correct
significant figures.
Answers
Answer:
37.5 g NaCl
Explanation:
Step 1: Given data
Concentration of NaCl: 15.0% m/mMass of the solution: 250.0 gStep 2: Calculate how many grams of NaCl are in 250.0 g of solution
The concentration of NaCl is 15.0% by mass, that is, there are 15.0 g of NaCl every 100 g of solution.
250.0 g Solution × 15.0 g NaCl/100 g Solution = 37.5 g NaCl
A sample of O2 gas is put into a bottle at STP. If the volume of the bottle is 0.52 L, how many moles of O2 will the bottle contain?
please help!!
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
So,at STP or NTP, one mole of any gas occupies 22.4 litres of volume. To find mass,firstly we have to calculate the no. Of moles present in 11.2 litres of O2 gas which can be calculated as ;
No. Of moles = Given Volume ÷ 22.4 Litre (provided that gas is at STP)
= 11.2 Litre / 22.4 Litre
= 0.5 moles
Now, mass can be calculated by;
Mass = no. Of moles × Molecular mass
= 0.5 × 32 (Molecular mass of O2 is 32u or 32 g, if you are calculating in Grams, also called Gram Molecular Mass)
= 16 g
This is the answer
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2
If 12 moles of Al completely react, how many moles of H2 are produced?
Answers
Answer:
18 moles of H₂.
Explanation:
The balanced equation for the reaction is given below:
2Al + 6HCl –> 2AlCl₃ + 3H₂
From the balanced equation above,
2 moles of Al reacted to produce 3 moles of H₂.
Finally, we shall determine the number of mole of H₂ produced by the reaction of 12 moles of Al. This can be obtained as follow:
From the balanced equation above,
2 moles of Al reacted to produce 3 moles of H₂.
Therefore, 12 moles of Al will react to produce = (12 × 3)/2 = 18 moles of H₂.
Thus, 18 moles of H₂ were obtained from the reaction.
How many grams of aluminum is required to react with 75.0 ml of 2.50 M HCl?
Answers
Answer:
63 g Al is required to react with 35 mL of 2.50 M hydrochloric acid
I'm sorry if it's wrong, I tried.
Explanation:
Calculate the molality of a solution that contains 75.0-grams of methyl alcohol, CH3OH, dissolved in 600.0-grams of
water.
Answers
Answer:
[tex]m=3.90mol/kg[/tex]
Explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, since the molality of a solution is calculated by dividing moles of solute by kilograms of solvent, it turns out firstly necessary for us to calculate the moles of methyl alcohol in 75.0 grams as shown below:
[tex]n=\frac{75.0g}{32.04g/mol}=2.34mol[/tex]
Then, the kilograms of water, 0.600 kg, and finally, the resulting molality:
[tex]m=\frac{2.34mol}{0.600kg}\\\\m=3.90mol/kg[/tex]
Regards!
How many molecules are in 4.44 mol of CF4? 4.44 mol CF4 =
Answers
Answer
Molecular Mass for CF4 = 88.004349 Da
I am not sure abt the ans
molar mass= 88
1 molecule = 6.022×10^23
4.44 moles = 6.022×10^23×4.44/88
= 26.73768 × 10^23/88
= 0.3038372727 ×10^23
The normal boiling point of a certain liquid X is 130.9 °C, but when 19.9 g of urea (NH2) CO are dissolved in 200. g of X, it is found that the solution boils at 134.1 °C instead. Use this information to calculate the molal boiling point elevation constant K, of X. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits x 1 ℃.mol -kg
Answers
Answer:
K = 1.93 °C/m
Explanation:
This question can be solved by formula of elevation of boiling point.
Boiling T° of solution - Boiling T° of pure solvent = K . m . i
Our solute is urea.
Our solvent is X.
We convert mass of urea to moles: 19.9 g . 1 mol / 60.06g = 0.331 mol
We convert g of solute to kg = 200 g . 1 kg/ 1000g = 0.2kg
m = molality → moles of solute / kg of solvent
m = 0.331 mol / 0.2 kg = 1.66 m
As urea is an organic compound, no ions will be formed.
i = 1 (a non ionizing compound)
Let's replace data in formula:
134,1°C - 130.9°C = K . 1.66 m . 1
3.2 °C / 1.66 m = K
K = 1.93 °C/m
Provide the IUPAC names for
the following structures
CH2CH3
w
CH2CH:
(b) H-C-N
CH.CH
H-EN
N
H
(c)
OCH2CH3
Answers
Answer:
For a: The IUPAC name of the compound is N-ethylethaneamide.
For b: The IUPAC name of the compound is N,N-diethylmethaneamide.
For c: The IUPAC name of the compound is ethyl pentanoate
Explanation:
To name a compound, first look for the longest possible carbon chain.
For a:Amide group is a type of functional group where an amine group is attached to a carbonyl group. The general formula of amide is [tex]R-CO-NH_2[/tex], where R is an alkyl or aryl group.
In part (a), the alkyl group has 2 carbon atoms and thus, the prefix used is 'eth-'
Also, an ethyl substituent is directly attached to N-atom. It is an alkane structured hydrocarbon thus, the suffix used will be '-ane'
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound is N-ethylethaneamide.
For b:Amide group is a type of functional group where an amine group is attached to a carbonyl group. The general formula of amide is [tex]R-CO-NH_2[/tex], where R is an alkyl or aryl group.
In part (b), the alkyl group has 1 carbon atoms and thus, the prefix used is 'meth-'
Also, two ethyl substituents are directly attached to N-atom. It is an alkane structured hydrocarbon thus, the suffix used will be '-ane'
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound is N,N-diethylmethaneamide.
For c:Esters are a kind of organic molecules having functional groups, [tex]R-COO-R'[/tex] where R and R' are the alkyl or aryl groups. They are formed by the combination of alcohol and carboxylic acid.
These functional group compounds are named in two words which is alkyl alkanoates, where alkyl refers to the alcoholic part and alkanoate refers to the carboxylic acid part of the molecule. The numbering of the parent chain in esters is done from the carboxylic carbon. The alkyl part is not given any numbers.
In part (c), there are 5 carbon atoms present in a straight chain and thus, the prefix used is 'pent-'
Also, an ethyl group forms the alcoholic part.
Hence, the IUPAC name of the compound is ethyl pentanoate
Which bodies of water in the list are found to the west of the Philippines?
Answers
Answer:
South China sea
Explanation:
To the west is the South China Sea, to the east the Philippine Sea and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south the Celebes Sea (or Sulawesi Sea).
The empirical formula of a compound with 4 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, and 2 oxygen atoms is
Answers
Answer:
c2h6o
Explanation:
find the hcf of the numbers and divide each number by the HCF eg
HCF of 4,12,2 -> 2
4÷2=2
12÷2=6
2÷2=1
therefore
c2h6o
The reaction of iron (III) oxide with carbon monoxide produces iron and carbon dioxide.
Fe2O3(s) + 3C0(9) - 2Fe(s) + 3CO (9)
How many grams of Fe2O3 are required to produce 4.65g Fe? You must show your work to receive full credit.
Answers
Answer:
6.65 grams of Fe₂O₃ are required to produce 4.65g Fe.
Explanation:
The balanced reaction is:
Fe₂O₃ + 3 CO → 2 Fe + 3 CO₂
By reaction stoichiometry (that is, the relationship between the amount of reagents and products in a chemical reaction), the following amounts of moles of each compound participate in the reaction:
Fe₂O₃: 1 moleCO: 3 molesFe: 2 molesCO₂: 3 molesThe molar mass of each compound is:
Fe₂O₃: 159.7 g/moleCO: 28 g/molFe: 55.85 g/moleCO₂: 44 g/moleThen, by reaction stoichiometry, the following mass quantities of each compound participate in the reaction:
Fe₂O₃: 1 mole* 159.7 g/mole= 159.7 gramsCO: 3 moles* 28 g/mol= 84 gramsFe: 2 moles* 55.85 g/mole= 111.7 gramsCO₂: 3 moles* 44 g/mole= 132 gramsThen you can apply the following rule of three: if by stoichiometry 111.7 grams of Fe are produced from 159.7 grams of Fe₂O₃, 4.65 grams of Fe are produced from how much mass of Fe₂O₃?
[tex]mass of Fe_{2} O_{3} =\frac{4.65 grams of Fe*159.7 grams of Fe_{2} O_{3}}{111.7grams of Fe}[/tex]
mass of Fe₂O₃= 6.65 grams
6.65 grams of Fe₂O₃ are required to produce 4.65g Fe.
Draw the diagram of 4-propylnonane
Answers
im missing something though
2
Drag the tiles to the correct locations on the equation. Not all tiles will be used.
Two atoms interact with each other as shown by the equation. Complete the equation by filling in the missing parts.
1
2
3
4
5
5
H
le
Li
?H + He -
+
TH
H
Reset
Next
Answers
Answer:
4 on the top
He in the middle
2 on the bottom
Explanation:
Correct on plato
The missing of the part of the chemical equation when the two atoms interact is Helium with mass number 4 and atomic number 2.
What is interaction of the two atoms?The two atoms interact with each other as shown by the equation below;
[tex]^4_2He[/tex]
where;
He is Helium atom4 is the mass number of the helium atom2 is the atomic number of the helium atom.Thus, the missing of the part of the chemical equation when the two atoms interact is Helium with mass number 4 and atomic number 2.
Learn more about helium atom here: https://brainly.com/question/26226232
#SPJ5
Se prepara una solución agregando sal en 500 g de agua. Calcular la masa de sal, cuando se tiene una solución al 6,4 % en masa
Answers
Answer:
x~ 34.19 grams del sal o ~ 34 grams!
Explanation:
el porcentaje de masa se escribe como
% de masa = masa de sal / (masa de sal + masa de disolvente) * 100%
aquí, el disolvente se da como 500 g de agua.
usa x en lugar de masa de sal y resuelve usando álgebra
6.4 = x / (x+ 500) * 100
0.064 = x / (x+500)
0.064 x + 32 = x
32 = x-0.064x
32 = 0.936 x
x~ 34.19 grams del sal o ~ 34 grams!
Write the Ka expression for an aqueous solution of hypochlorous acid: (Note that either the numerator or denominator may contain more than one chemical species. Enter the complete numerator in the top box and the complete denominator in the bottom box. Remember to write the hydronium ion out as , and not as )
Answers
Answer: The Ka expression for an aqueous solution of hypochlorous acid is [tex]K_{a} = \frac{[H_{3}O^{+}][OCl^{-}]}{[HClO]}[/tex].
Explanation:
The chemical formula of hypochlorous acid is HClO. So, when it is added to water (solvent) then its dissociation is as follows.
[tex]HClO + H_{2}O \rightarrow H_{3}O^{+} + Cl^{-}[/tex]
When we write the equilibrium constant for this reaction then it is called acid acid dissociated constant.
Hence, the expression for acid dissociation constant of this reaction is as follows.
[tex]K_{a} = \frac{[H_{3}O^{+}][OCl^{-}]}{[HClO]}[/tex]
Thus, we can conclude that the Ka expression for an aqueous solution of hypochlorous acid is [tex]K_{a} = \frac{[H_{3}O^{+}][OCl^{-}]}{[HClO]}[/tex].
Calcium carbonate is often used as an antacid. Your stomach acid is composed of HCl at a pH of 1.5. If you ate toooo much Turkey and need to neutralize 15.0 mL of stomach acid, how many grams of calcium carbonate would you need to take
Answers
Answer: 0.0237 g of calcium carbonate would be required to neutralize the given amount of HCl
Explanation:
pH is defined as the negative logarithm of hydrogen ion concentration present in the solution
[tex]pH=-\log [H^+][/tex] .....(1)
Given value of pH = 1.5
Putting values in equation 1:
[tex]1.5=-\log[H^+][/tex]
[tex][H^+]=10^{(-1.5)}=0.0316M[/tex]
Molarity is defined as the amount of solute expressed in the number of moles present per liter of solution. The units of molarity are mol/L. The formula used to calculate molarity:
[tex]\text{Molarity of solution}=\frac{\text{Number of moles of solute}\times 1000}{\text{Volume of solution (mL)}}[/tex] .....(2)
We are given:
Volume of solution = 15.0 mL
Molarity of HCl = 0.0316 M
Putting values in equation 2:
[tex]0.0316=\frac{\text{Moles of HCl}\times 1000}{15.0}\\\\\text{Moles of HCl}=\frac{0.0316\times 15.0}{1000}=4.74\times 10^{-4}mol[/tex]
The chemical equation for the reaction of HCl and calcium carbonate follows:
[tex]2HCl+CaCO_3\rightarrow H_2CO_3+CaCl_2[/tex]
By the stoichiometry of the reaction:
2 moles of HCl reacts with 1 mole of calcium carbonate
So, [tex]4.74\times 10^{-4}mol[/tex] of HCl will react with = [tex]\frac{1}{2}\times 4.74\times 10^{-4}=2.37\times 10^{-4}mol[/tex] of calcium carbonate
The number of moles is defined as the ratio of the mass of a substance to its molar mass.
[tex]\text{Number of moles}=\frac{\text{Given mass}}{\text{Molar mass}}[/tex]
Moles of calcium carbonate = [tex]2.37\times 10^{-4}mol[/tex]
Molar mass of calcium carbonate = 100.01 g/mol
Putting values in the above equation:
[tex]\text{Mass of }CaCO_3=(2.37\times 10^{-4}mol)\times 100.01g/mol\\\\\text{Mass of }CaCO_3=0.0237g[/tex]
Hence, 0.0237 g of calcium carbonate would be required to neutralize the given amount of HCl
How would the accuracy of your determined Keq change if all of your volume measurements were made with graduated cylinders rather than pipets
Answers
Answer:
Accuracy decreases
Explanation:
All meaurements have an uncertainty (That is, the error of the measurement). The uncertainty of graduated cylinders is higher than uncertainty of pipets.
The accuracy is how close is the measurement to the real value.
If you use graduated cylinders rather than pipets, accuracy decreases because you will have more uncertainty in the measurements putting of the real value and the real value.
The accuracy of the determined value decreases if all measurement is done with graduated cylinders.
What is Accuracy?The accuracy is the measurement of how close the calculated value is to the real value.
When a student measures the volume with a graduated cylinder the chances of error increase.
Therefore, the accuracy of the determined value decreases if all measurement is done with graduated cylinders.
Learn more about accuracy:
https://brainly.com/question/24869562
If the pH of a solution increases from 4.0 to 6.0, the hydronium ion concentration.
A) increases by a factor of 100.
B) decreases by a factor of a 100.
C) decreases by a factor of 1.5
D) increases by a factor of 1.5
Answers
Answer:
decrease by a factor of 1.5
Select the correct answer.
Which value of Keq represents a scenario where the reactants of an equilibrium reaction are favored?
A.
Keq=1
B.
Keq = 6.0 x 10-2
O C.
Keq = 3.8 x 104
OD
Keq = 490.5
O E. Keq = 2.5
Answers
Answer:
B. Keq = 6.0 x 10-2.
Explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given information, it turns out possible for us to remember that any equilibrium constant is computed by dividing the concentration of products by that of reactants:
[tex]Keq=\frac{[Prod]}{[Reac]}[/tex]
Thus, a reaction that is reactant-favored will have a Keq>1 because the concentration of reactants prevail over that of products at equilibrium, and thus, the correct answer is B. Keq = 6.0 x 10-2.
Regards!
1.00 mL of 12.0 M HCl is added to 1.00 L of a buffer that contains 0.110 M HNO2 and 0.170 M NaNO2. How many moles of HNO2 and NaNO2 remain in solution after addition of the HCl
Answers
Answer:
Moles of NaNO2 = 0.158
Moles of HNO2 final = 0.098
Explanation:
Given
Moles of HCl = 12
Moles of HNO2 = 0.11
Moles of NaNO2 = 0.170
HCl +NaNO2 --> HNO2 + NaCl
1 mole of HCl react with one mole of NaNO2 to produce 1 mole of NaCl and 1 mole of HNO2
Moles of NaNO2 = 0.17 - 0.012 = 0.158
Moles of HNO2 final = 0.11 - 0.012 = 0.098