Reliable Corporation provides computer consulting services to the local community and keeps its accounting records using cash-basis accounting. For the current year, cash was received from customers, $48,000, and cash salaries to employees were paid, $26,000. At the beginning of the year, customers owe Reliable $1,200. By the end of the year, customers owe $7,600. At the beginning of the year, Reliable owes employee salaries of $6,600. At the end of the year, Reliable owes employee salaries of $3,800. Determine cash-basis net income and accrual-basis net income for the current year.
Answers
Answer:
Net Income as per the Cash Basis Accounting $22,000
Net Income as per the Accrual Basis Accounting is $31,200
Explanation:
The cash basis accounting says that the net income is the cash left after the difference in the net cash inflow and cash outflow.
Mathematically,
Net Income By Using Cash Basis Accounting = Net Cash Inflow - Net Cash Outflow
Here
Net Cash Inflow is $48,000
Net Cash Outflow is $26,000
By putting values, we have:
Net Income By Using Cash Basis Accounting = $48,000 - $26,000
= $22,000
Now, when we are using accrual accounting then the first thing we should know is that whether the expense or income is related to the period or not. If the income is related to the period, then it must be included in the income and if it is not then it will be excluded. The same is with the expenses.
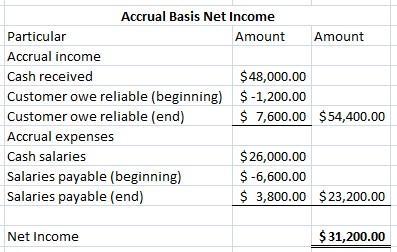
Accrual Income Computation:
Cash Received for the year is $48000 which will be included.
The receiveable amount of $1200 is for the previous period which means it will be excluded.
Furthermore, the receivable amount of $7600 includes $1200 of the previous month which means the difference ($6400) would be included.
This implies that
Accrual Income For The Period = $48000 + $6400 = $54,400
Now Accrual Expense Computation:
The cash salaries of $26000 paid to employees will be included.
The salaries payable of $6600 belongs to the previous period which means it must not be included.
The closing salaries payable is $3800 which means that the difference of opening and closing which is $2800, was paid against the previous month and hence must be deducted from the cash salaries for the period.
This implies that
Accrued Expense For The Period = $26000 - $2800 = $23200
Finally,
Net Accrued Income = $54,400 - $23,200 = $31,200
The net income is the income amount earned at the year-end. The amount of net income by cash basis is $22,000, while the net income by accrual basis is $23,200.
What is net income?The net income is the remaining amount of income with the business at the year-end. It is determined by deducting all the operating and non-operating expenses from the total income earned during the specified period.
The computation of net income by using cash basis accounting:
[tex]\begin{aligned}\text{Net Income}&=\text{Net Cash Inflow}-\text{Net Cash Outflow}\\&=\$48,000-\$26,000\\&=\$22,000\end{aligned}[/tex]
The computation of net income by using accrual basis accounting is shown in the image attached below.
Therefore, the net income is $22,000 by cash basis accounting and $23,200 in accrual basis accounting.
Learn more about net income, here:
https://brainly.com/question/25247632
Related Questions
The 2021 income statement of Adrian Express reports sales of $20,710,000, cost of goods sold of $12,600,000, and net income of $1,980,000. Balance sheet information is provided in the following table.
ADRIAN EXPRESS
Balance Sheets
December 31, 2021 and 2020
2021 2020
Assets
Current assets:
Cash $840,000 $930,000
Accounts receivable 1,775,000 1,205,000
Inventory 2,245,000 1,675,000
Long-term assets 5,040,000 4,410,000
Total assets $ 9,900,000 $8,220,000
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity
Current liabilities $ 2,074,000 $1,844,000
Long-term liabilities 2,526,000 2,584,000
Common stock 2,075,000 2,005,000
Retained earnings 3,225,000 1,787,000
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity
$9,900,000 $8,220,000
Industry averages for the following profitability ratios are as follows:
Gross profit ratio 45 %
Return on assets 25 %
Profit margin 15 %
Asset turnover 8.5 times
Return on equity 35 %
Required:
1. Calculate the five profitability ratios listed above for Adrian Express. (Round your answers to 1 decimal place.)
2. Do you think the company is more profitable or less profitable than the industry average?
More profitable
Less profitable
Answers
Answer:
Adrian Express
1. Five Profitability Ratios:
Gross profit ratio: = 39.2%
Return on assets = 20%
Profit margin = 9.6%
Asset turnover = 2.1 times
Return on equity = 37.4%
2. I think the company is:
Less profitable
than the industry average.
Explanation:
a) Data and Calculations:
Sales Revenue $20,710,000
Cost of goods sold $12,600,000
Gross profit $8,110,000
Net income $1,980,000
ADRIAN EXPRESS
Balance Sheets
December 31, 2021 and 2020
2021 2020
Assets
Current assets:
Cash $840,000 $930,000
Accounts receivable 1,775,000 1,205,000
Inventory 2,245,000 1,675,000
Current assets $4,860,000 $3,810,000
Long-term assets 5,040,000 4,410,000
Total assets $ 9,900,000 $8,220,000
Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity
Current liabilities $ 2,074,000 $1,844,000
Long-term liabilities 2,526,000 2,584,000
Common stock 2,075,000 2,005,000
Retained earnings 3,225,000 1,787,000
Total Equity 5,300,000 3,792,000
Total liabilities & stockholders' equity $9,900,000 $8,220,000
Industry averages for the following profitability ratios are as follows:
Gross profit ratio 45 %
Return on assets 25 %
Profit margin 15 %
Asset turnover 8.5 times
Return on equity 35 %
Gross profit ratio: = Gross profit/Sales * 100
= $8,110,000/$20,710,000 * 100
= 39.2%
Return on assets = Net income/Assets * 100
= $1,980,000/$9,900,000 * 100
= 20%
Profit margin = Net Income/Sales * 100
= $1,980,000/$20,710,000 * 100
= 9.6%
Asset turnover = Sales/Total Assets
= $20,710,000/$9,900,000 = 2.1 times
Return on equity = Net Income/Total Equity * 100
= $1,980,000/$5,300,000 * 100
= 37.4%
Predetermined Overhead Rate, Application of Overhead to Jobs, Job Cost
On April 1, Sangvikar Company had the following balances in its inventory accounts:
Materials Inventory $12,750
Work-in-Process Inventory 21,060
Finished Goods Inventory 8,500
Work-in-process inventory is made up of three jobs with the following costs:
Job 114 Job 115 Job 116
Direct materials $2,384 $2,603 $3,085
Direct labor 1,800 1,420 4,420
Applied overhead 1,260 994 3,094
During April, Sangvikar experienced the transactions listed below.
Materials purchased on account, $28,920.
Materials requisitioned: Job 114, $16,800; Job 115, $12,460; and Job 116, $5,410.
Job tickets were collected and summarized: Job 114, 170 hours at $11 per hour; Job 115, 200 hours at $14 per hour; and Job 116, 100 hours at $19 per hour.
Overhead is applied on the basis of direct labor cost.
Actual overhead was $4,535.
Job 115 was completed and transferred to the finished goods warehouse.
Job 115 was shipped, and the customer was billed for 125 percent of the cost.
Required:
1. Calculate the predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor cost.
% of direct labor cost
2. Calculate the ending balance for each job as of April 30. When required, round your answers to the nearest dollar. Use your rounded answers in subsequent computations, if necessary.
Ending Balance
Job 114 $
Job 115 $
Job 116 $
3. Calculate the ending balance of Work in Process as of April 30. When required, round your answer to the nearest dollar.
$
4. Calculate the cost of goods sold for April. When required, round your answer to the nearest dollar.
$
5. Assuming that Sangvikar prices its jobs at cost plus -25 percent, calculate the price of the one job that was sold during April. Round to the nearest dollar.
$
Answers
Answer:
See below
Explanation:
1. Predetermined overhead rates
= Applied overhead / Direct labor
Job 114
Applied overhead / direct labor
= $1,260/1,800
= 70%
Job 115
Applied overhead / direct labor
= $994/1,420
= 70%
Job 116
Applied overhead / direct labor
= $3,094/4,420
= 70%
2 and 3 Ending balance of each job and work in process as of April 30th.
Job 114. Job116
Opening. $2,384. $3,085
Materials
Purchases $16,800. $5,410
Direct labor
($1,800+$1,800) $3,600. $5,740
Actual $2,520 $4,018
Overhead
at 59.36%
Balance $25,304. $18,253
• Note
The whole of job 115 has been sold out.
• Actual overhead = Actual overhead / direct labor
= $4,535/7,640
= 59.36%
4 Cost of goods sold in April
Job 115
Opening materials. $2,603
Purchases. $12,460
Direct labor
($1,420 + $3,080). $4,500
Actual overhead. $3,150
at 59.36%
Cost of goods sold $22,713
5. Selling price of job
Cost of job 115 = $22,713
Selling price = 1.25% × $22,713 = $28,391
Whirly Corporation’s contribution format income statement for the most recent month is shown below: Total Per Unit Sales (7,600 units) $ 250,800 $ 33.00 Variable expenses 144,400 19.00 Contribution margin 106,400 $ 14.00 Fixed expenses 54,800 Net operating income $ 51,600 Required: (Consider each case independently): 1. What would be the revised net operating income per month if the sales volume increases by 70 units? 2. What would be the revised net operating income per month if the sales volume decreases by 70 units? 3. What would be the revised net operating income per month if the sales volume is 6,600 units?
Answers
Answer:
1. What would be the revised net operating income per month if the sales volume increases by 70 units?
Sales total (7,670*$33) $253,110
Less: Variable expenses (7,670*$19) $145,730
Contribution margin $107,380
Less: Fixed expenses $54,800
Net operating income $52,580
2. What would be the revised net operating income per month if the sales volume decreases by 70 units?
Sales total (7530*$33) $248,490
Less: Variable expenses (7530*$19) $143,070
Contribution margin $105,420
Less: Fixed expenses $54,800
Net operating income $50,620
3. What would be the revised net operating income per month if the sales volume is 6,600 units?
Sales total (6,600*$33) $217,800
Less: Variable expenses (6,600*$19) $125,400
Contribution margin $92,400
Less: Fixed expenses $54,800
Net operating income $37,600
Multiple Choice Question Valpar Company produces several lines of laundry hampers. The factory is highly automated and uses an activity-based costing system to allocate overhead costs to its various products. During the upcoming period the company expects to produce 72,000 units. The costs and cost drivers associated with four activity cost pools are given below: Activities Unit Level Batch Level Product Level Facility Level Cost $20,000 $10,000 $15,000 $36,000 Cost Driver 4,000 labor hours 400 set-ups % of use 72,000 units Production of 20,000 units of its popular foldable hamper required 2,000 labor hours, 20 setups, and consumed one-quarter of the product sustaining activities. What amount of batch-level costs will be allocated to the product
Answers
Answer:
$500
Explanation:
Calculation to determine the amount of batch-level costs that will be allocated to the product
Using this formula
Allocation rate=(Total batch level overhead cost/Total activity base ) * Set-ups
Let plug in the formula
Allocation rate=( $10,000/400 set-ups) *20 set-ups
Allocation rate=$25 per set-up *20 set-ups
Allocation rate=$500
Therefore the amount of batch-level costs that will be allocated to the product is $500
Assume Dell's yearly inventory cost is 30 percent to account for the cost of capital for financing the inventory, the warehouse space, and the cost of obsolescence. In other words, Dell incurs a cost of $30 for a $100 component that is in the company's inventory for one entire year. In 2001, Dell's 10-k reports showed that the company had $280 million in inventory and COGS of $23,100 million. To compute the percentage of cost of the inventory, determine the following:
a. Find the value of the inventory.
b. Find the cost of goods sold.
c. Compute inventory turns. (Round the answer to the nearest whole number.)
d. What percentage of cost of a Dell computer reflects inventory costs? (Round the answer to 3 decimal places.)
Answers
Answer:
See below
Explanation
1. Value of inventory sold
= $280 million in inventory + COGS $23,100 million
= $303,100 million
2. Cost of goods sold
From the above passage, we have been given the COGS , which is $23,100 million
3. Compute inventory turns
= Cost of goods sold / Average stock
= $23,100 million / $151,550
=
define securitization.
Answers
Answer:
The conversion of an asset, especially a loan, into marketable securities, typically for the purpose of raising cash by selling them to other investors.
All of the following are benefits associated with empowerment except: a. empowered employees are more likely to respond in a positive way to service failures and to engage in effective service recovery strategies. b. empowered employees are more customer focused and quicker in responding to customer needs. c. empowered employees tend to feel better about their jobs and themselves, which is automatically reflected in the way they interact with customers. d. empowered front-line employees gain a false sense of power, in turn aiding the customer. e. empowered front-line service employees can be key to new service ideas and a cheaper source of market research than going to the consumer directly.
Answers
Answer:
d. empowered front-line employees gain a false sense of power, in turn aiding the customer.
Explanation:
Employee empowerment is when an employer gives the employee a degree of autonomy in making decisions that affects their jobs.
They are allowed to decide how best to perform their jobs.
This gives the employee a sense of ownership that translates to better customer service, positive attitude, better employee moral, and cheaper source of market research than going to the consumer directly.
However this style does not give a false sense to power, because the employees actually.have autonomy in their work.
The statement that does not benefits associated with empowerment is that empowered front-line employees gain a false sense of power, in turn aiding the customer.
Empowerment is known to be firm based commitment to respect all its employees as intelligent and responsible human beings.The rewards of empowerment are numerous such as higher levels of employee satisfaction, a sense of shared purpose, and more collaboration etc.
Conclusively ,Employee empowerment as a management philosophy uses the importance of granting employees to make independent decisions and act on them.
Learn more from
https://brainly.com/question/24113378
With regard to the types of interviews: A. Reference-based interviews are best at predicting sales success. B. Situation-based interviews pose questions about past situations to predict how the candidate might respond in the future. C. Behavior and situation based interviews are highly unstructured. D. Performance based interviews are interviews conducted by senior salespeople in the field. E. None of these is correct.
Answers
Answer:
can you put a picture might be easier to read it
The statement that asserts a true claim regarding kinds of interviews would be:
E). None of these is correct.
What is an Interview?
"Interview" is described as the conversation that is taken personally and a set of questions have been asked for a publication or channel.
The given statements assert incorrect claims regarding the various types of interviews.
The reference-based interviews are taken when a person is referred by another to get a better understanding of the caliber and capability of his/her.
While Situation-based interviews pose a hypothetical situation and behavior interviews observe particular behavioral patterns.
Thus, option E is the correct answer.
Learn more about "Interview" here:
brainly.com/question/7638386
define moral hazard.
Answers
Answer:
Moral hazard is type of situation in where on person or party gets involved in a very risky event when knowing that it is protected against and the person or party, which will incur the cost. This can arise when both people or parties have a incomplete information about on another or each other.
An error in the ending inventory balance in Year 1 will also affect: (You may select more than one answer. Single click the box with the question mark to produce a check mark for a correct answer and double click the box with the question mark to empty the box for a wrong answer. Any boxes left with a question mark will be automatically graded as incorrect.)
1. Year 1 cost of goods soldunanswered
2. Year 2 cost of goods soldunanswered
3. Year 2 ending inventoryunanswered
4. Year 2 beginning inventory
Answers
Answer:
1. Year 1 cost of goods sold
2. Year 2 cost of goods sold
4. Year 2 beginning inventory
Explanation:
If year 1's ending inventory is wrong, the beginning inventory of year 2 will also be wrong (they are the same).
Cost of goods sold = cost of goods available for sale - ending inventory, so COGS for year 1 will be affected since ending inventory is wrong
Cost of goods available for sale = beginning inventory + purchases - ending inventory. Since beginning inventory year 2 is wrong, the cost of goods available for sale will also be wrong, as well as COGS
Which of the following will not cause the production possibility frontier to shift? Group of answer choices the introduction of "fiber optic" technology a land reclamation program an increase in the working population a reduction in unemployment an explosion destroying a chemical plant
Answers
Answer:
an increase in the working population
Explanation:
The Production possibilities frontier (PPF) is a curve that shows the various combination of two goods a company can produce when all its resources are fully utilised.
The PPC is concave to the origin. This means that as more quantities of a product is produced, the fewer resources it has available to produce another good. As a result, less of the other product would be produced. So, the opportunity cost of producing a good increase as more and more of that good is produced.
The PPF can shift either inward or outward.
An outward shift is associated with an increase in output while an inward shift is associated with a reduction in output.
Factors that cause the PPF to shift
1. changes in technology. technological progress leads to outward shift of the PPF. introduction of "fiber optic" technology would shift the PPF outward.
2. changes in available resources. a land reclamation program would increase the land available for production and this would increase output. While an explosion destroying a chemical plant would reduce output and lead to an inward shift of the PPF
3. changes in the labour force. A decrease in unemployment would increase output and shift the the PPF outward
Working population is the number of people between 15-59.
what is job description
Answers
A job description or JD is a written narrative that describes the general tasks, or other related duties, and responsibilities of a position. It may specify the functionary to whom the position reports, specifications such as the qualifications or skills needed by the person in the job, information about the equipment, tools and work aids used, working conditions, physical demands, and a salary range. Job descriptions are usually narrative,[1] but some may comprise a simple list of competencies; for instance, strategic human resource planning methodologies may be used to develop a competency architecture for an organization, from which job descriptions are built as a shortlist of competencies.[2][not specific enough to verify]
According to Torrington, a job description is usually developed by conducting a job analysis, which includes examining the tasks and sequences of tasks necessary to perform the job. The analysis considers the areas of knowledge, skills and abilities needed to perform the job. Job analysis generally involves the following steps: collecting and recording job information; checking the job information for accuracy; writing job descriptions based on the information; using the information to determine what skills, abilities, and knowledge are required to perform the job; updating the information from time to time. [3] A job usually includes several roles. According to Hall, the job description might be broadened to form a person specification or may be known as "terms of reference". The person/job specification can be presented as a stand-alone document, but in practice it is usually included within the job description. A job description is often used by employers in the recruitment process.
A job description is concerned with addressing the following issues about the job:
Job titleJob locationJob summaryWorking environmentDuties or tasks.What is the role of a job description?In addition to being concerned with the above-stated issues, a job description helps management to identify the job specifications, including the environmental pressures that apply to the position.
A job description also provides the measurement criteria for performance evaluations of each job holder.
Thus, a job description addresses job-related issues.
Learn more about job descriptions at https://brainly.com/question/4677114
The total of the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger must equal?
Answers
Consider a firm with $9,331 in current assets. The firm also has gross property plant and equipment of $1,717, depreciation expense of $9,780. The firm decided to reduce their capital structure and hold $0 in notes payable, $5,189 in accruals and $7,224 in accounts payable. The firm has $924 in long-term debt, $1,493 in interest expense. Calculate the firm's Total Assets
Answers
Answer:
$11,048
Explanation:
Total Assets = Current Assets + Non - Current Assets
= $11,048
An investor, such as a bank, may prefer to invest in securities backed by a pool of mortgages purchased in the secondary market rather than in an equal dollar amount of mortgage loans because:_________
a. mortgage backed securities eliminate prepayment risk for the investor.
b. mortgage backed securities diversify credit risk for the investor.
c. mortgage backed securities offer higher yields than individual mortgages.
d. mortgage backed securities returns are tax-exempt.
Answers
Answer:
b. mortgage backed securities diversify credit risk for the investor.
Explanation:
An investor, such as a bank, may prefer to invest in securities backed by a pool of mortgages purchased in the secondary market rather than in an equal dollar amount of mortgage loans because mortgage backed securities diversify credit risk for the investor.
In Mortgage Backed Securities, credit risk is diversified as there are many borrowers and investors between whom credit risk diversifies. So that makes investor such as bank prefer the option.
Shao Airlines is considering the purchase of two alternative planes. Plane A has an expected life of 5 years, will cost $100 million, and will produce net cash flows of $28 million per year. Plane B has a life of 10 years, will cost $132 million, and will produce net cash flows of $27 million per year. Shao plans to serve the route for only 10 years. Inflation in operating costs, airplane costs, and fares are expected to be zero, and the company's cost of capital is 9%. By how much would the value of the company increase if it accepted the better project (plane)
Answers
Answer:
41.28 million
Explanation:
the net present value of the two alternatives needs to be determined. The appropriate alternative would be the plane with the higher NPV
Net present value is the present value of after-tax cash flows from an investment less the amount invested.
NPV can be calculated using a financial calculator
Alternative 1
Cash flow in year 0 = $-100 million
Cash flow each year from year 1 to 5 = $28 million
I = 9%
NPV = $8.91 million
Alternative 2
Cash flow in year 0 = $-132 million
Cash flow each year from year 1 to 10 = $27 million
I = 9%
NPV = $41.28 million
The second alternative has the higher NPV and it would increase the value of the company by $41.28 million if accepted
To find the NPV using a financial calculator:
1. Input the cash flow values by pressing the CF button. After inputting the value, press enter and the arrow facing a downward direction.
2. after inputting all the cash flows, press the NPV button, input the value for I, press enter and the arrow facing a downward direction.
3. Press compute
How would the Security Market Line be affected, other things held constant, if the expected inflation rate decreases and investors also become more risk averse? a. The y-axis intercept would decline, and the slope would increase. b. The x-axis intercept would decline, and the slope would increase. c. The y-axis intercept would increase, and the slope would decline. d. The SML would be affected only if betas changed. e. Both the y-axis intercept and the slope would increase, leading to higher required returns.
Answers
Answer: a. The y-axis intercept would decline, and the slope would increase.
Explanation:
The security market line is simply refered to as the graphical representation of a CAPM which is the capital asset pricing model and it simply shows the market risk, of the securities in the market which is then plotted against the market return.
When the expected inflation rate decreases and the investors also become more risk averse, the Security Market Line would be affected, as the y-axis intercept would decline, and the slope would increase.
c. In 2018, preferred shareholders elected to convert 4.58 million shares of preferred stock ($39 million book value) into common stock. Rather than issue new shares, the company granted 4.58 million shares held in treasury stock to the preferred shareholders, with a total cost of $33 million. Prepare a journal entry to illustrate how this transaction would have been recorded. (Hint: use the cost per share for 2018 determined in b.) Enter answers in millions. Round to the nearest million.
Answers
Answer:
Dr Preferred stock 39
Cr Treasury stock 33
Cr Additional paid in capital 6
Explanation:
Since the value of preferred stock is lower than the value of treasury stock, then the difference must be recorded as additional paid in capital. Additional paid in capital = $39,000,000 - $33,000,000 = $6,000,000
Income Statement Project
2018 2019 2020
Revenue:
Book Sales
Ticket Sales
Total Revenue:
Expenses:
Salary
Depreciation
Supplies
Rent Insurance
Total Expense:
Net Income/Loss:
Directions: Build an income statement using the steps provided below.
1) The book store received $50,000 in book sales for 2018, with a 20% increase in revenue each year.
2) Jack's book store received $15,000 each year in ticket sales to book signing events.
3) Find the Total Revenue each year for 2018-2020 using cell referencing.
4) Jack's book store paid $16,000 in employee salaries in 2018. Each year his employee salary cost increased by 25%.
*5) Jack purchased store furniture for $25,000 that is expected to be used over the next 5 years.
6) Jack bought $3,000 in supplies in 2018 and supplies costing $1,000 were used up each year.
'7) Jack signed a contract to pay $800/month for rent between 2018-2020.
8) Jack's book store pays $500 each month to cover insurance.
9) Find the Total Expense each year for 2018-2020 using the SUM function.
10) Find the Net Income/Loss using cell referencing.
Answers
Answer:
Jack's Bookstore
Income Statement Projection:
2018 2019 2020
Revenue:
Book Sales $50,000 $60,000 $72,000
Ticket Sales 15,000 15,000 15,000
Total Revenue: $65,000 $75,000 $87,000
Expenses:
Salary $16,000 $20,000 $25,000
Depreciation 5,000 5,000 5,000
Supplies 1,000 1,000 1,000
Rent 9,600 9,600 9,600
Insurance 6,000 6,000 6,000
Total Expense: $37,600 $41,600 $46,600
Net Income/Loss: $27,400 $33,400 $40,400
Explanation:
a) Data and Calculations:
Book Sales for 2019 = $60,000 ($50,000 * 1.20)
Book Sales for 2020 = $72,000 ($60,000 * 1.20)
Salaries for 2019 = $20,000 ($16,000 * 1.25)
Salaries for 2020 = $25,000 ($20,000 * 1.25)
Depreciation expense per year = $5,000 ($25,000/5) using the straight-line method
Supplies Expense per year = $1,000 ($3,000/3)
Rent Expense per year = $9,600 ($800 * 12)
Insurance Expense per year = $6,000 ($500 * 12)
true or false. the demand curve for the product of a monopolist is the same as the demand curve for the industry.
Answers
ose purchased a vehicle for business and personal use. In 2020, he used the vehicle 10,500 miles (80% of total) for business and calculated his vehicle expenses using the standard mileage rate (mileage was incurred ratably throughout the year). He paid $850 in interest and $85 in property taxes on the car. Required: Calculate the total business deduction related to the car. (Round your final answers to nearest whole dollar amount.)
Answers
Answer:
$6,366
Explanation:
Calculation for the total business deduction related to the car:
Total business deduction=($10,500x .535) + $850(.80) + $85(.80)
Total business deduction=$5,618+$680+$68
Total business deduction=$6,366
Therefore the total business deduction related to the car is $6,366
Cypress Oil Company's December 31, 2021, balance sheet listed $855,000 of notes receivable and $22,500 of interest receivable included in current assets. The following notes make up the notes receivable balance: Note 1 Dated 8/31/2021, principal of $400,000 and interest at 12% due on 2/28/2022. Note 2 Dated 6/30/2021, principal of $260,000 and interest due 3/31/2022. Note 3 $200,000 face value noninterest-bearing note dated 9/30/2021, due 3/31/2022. Note was issued in exchange for merchandise.
The company records adjusting entries only at year-end. There were no other notes receivable outstanding during 2021.
Required:
1. Determine the rate used to discount the noninterest-bearing note.
2. Determine the explicit interest rate on Note 2. (Round your intermediate calculations to the nearest whole dollar amount.)
3. What is the amount of interest revenue that appears in the company’s 2021 income statement related to these notes?
Discount rate
Interest rate
Interest revenue
Answers
Answer:
1. Determine the rate used to discount the noninterest-bearing note.
face value of the notes receivable = $400,000 + $260,000 + $200,000 = $860,000
carrying value = $855,000
difference = $860,000 - $855,000 = $5,000
6 month note, so total interest = $10,000
yearly interest = $10,000 x 2 = $20,000
interest rate = $20,000 / $200,000 = 10%
2. Determine the explicit interest rate on Note 2. (Round your intermediate calculations to the nearest whole dollar amount.)
total accrued interest = $22,500
interest on note 1 = $16,000
interest on note 2 = $6,500 (six months worth of interest)
total yearly interest = $13,000
interest rate = $13,000 / $260,000 = 5%
3. What is the amount of interest revenue that appears in the company’s 2021 income statement related to these notes?
total interest = $22,500 + $5,000 = $27,500
Delisa Corporation has two divisions: Division L and Division Q. Data from the most recent month appear below: Total Company Division L Division Q Sales $490,000 $125,000 $365,000 Variable expenses 288,800 62,500 226,300 Contribution margin 201,200 62,500 138,700 Traceable fixed expenses 111,650 34,790 76,860 Segment margin 89,550 $ 27,710 $ 61,840 Common fixed expenses 36,910 Net operating income $ 52,640 The break-even in sales dollars for Division Q is closest to:
Answers
Answer:
Break-even point (dollars)= $202,263.16
Explanation:
Giving the following information:
Division Q:
Sales= $365,000
Total variable costs= 226,300
Fixed costs= 76,860
To calculate the break-even point for Division Q, we need to use the following formula:
Break-even point (dollars)= fixed costs/ contribution margin ratio
Break-even point (dollars)= 76,860 / [(365,000 - 226,300) / 365,000]
Break-even point (dollars)= 76,860 / 0.38
Break-even point (dollars)= $202,263.16
Celestin Manufacturing Company incurred $22,000 of depreciation on its manufacturing equipment during its first year of operation. During this year the company made 11,000 units of product and sold 3,700 units of product. Based on this information alone the company would show Multiple Choice $22,000 of depreciation expense on its income statement. $7,400 of cost of goods sold expense on its income statement. $22,000 of inventory on its balance sheet. $7,400 of inventory on its balance sheet.
Answers
Answer:
$7400 of cost of goods sold expense on its income statement.
Explanation:
Calculation to determine the cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold expense=($22000 / 11000 units)x 3,700 units sold
Cost of goods sold expense= $2 per unit x 3,700 units sold
Cost of goods sold expense=$7400
Therefore Based on this information alone the company would show: $7400 of cost of goods sold expense on its income statement.
Pharoah Corporation factors $251,700 of accounts receivable with Kathleen Battle Financing, Inc. on a with recourse basis. Kathleen Battle Financing will collect the receivables. The receivables records are transferred to Kathleen Battle Financing on August 15, 2020. Kathleen Battle Financing assesses a finance charge of 2% of the amount of accounts receivable and also reserves an amount equal to 4% of accounts receivable to cover probable adjustments. (b) Assume that the conditions are met for a transfer of receivables with recourse to be accounted for as a sale. Prepare the journal entry on August 15, 2020, for Pharoah to record the sale of receivables, assuming the recourse obligation has a fair value of $5,010. (If no entry is required, select "No Entry" for the account titles and enter 0 for the amounts. Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually.)
Answers
Answer:
Cash received (251,700*94%) $236,598
Add: Due from factor (251,700*4%) $10,068
Less: Recourse obligation $5,010
Net proceeds $241,656
Gain/Loss = Carrying value - Net proceeds
Gain = $251,700 - $241,656
Gain = $10,044
Journal entry
Date Account Titles Debit Credit
Aug 15,2020 Cash $236,588
Due from factors $10,068
Gain on sale of receivables $10,044
Recourse liability $5,010
Account receivable $251,700
Costs associated with two alternatives, code-named Q and R, being considered by Albiston Corporation are listed below: Alternative Q Alternative R Supplies costs $ 74,000 $ 74,000 Power costs $ 34,200 $ 33,400 Inspection costs $ 27,000 $ 33,400 Assembly costs $ 39,000 $ 39,000 Required: a. Which costs are relevant and which are not relevant in the choice between these two alternatives
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Relevant costs are the costs which are affected by the decisions made by the management of an organization while irrelevant costs do not change in future as they're not affected by the decisions from the management.
Based on the information given, the relevant cost are:
1. Power cost
2. Inspection cost
The non relevant cost are:
1. Supplies cost
2. Assembly cost
1 - Describe two justifications for the need for professional financial planning advice
2- Summarize the main fees a mutual fund investor will pa
3 - Your client is asking how much life insurance she needs. She expects to earn $120,000 per year on average, working for the next 30 years.
a. Suppose an appropriate earnings multiple is 18. How much life insurance should she purchase? (2 points)
b. Using a discount rate of 4%, what is her insurance need using the human value approach? (3 points)
Answers
Answer:
Financial planning is a step-by-step approach to meet one's life goals. A financial plan acts as a guide as you go through life's journey. Essentially, it helps you be in control of your income, expenses and investments such that you can manage your money and achieve your goals.
Explanation:
Gibson Corp. owned a 90% interest in Sparis Co. Sparis frequently made sales of inventory to Gibson. The sales, which include a markup over cost of 25%, were $420,000 in 2017 and $500,000 in 2018. At the end of each year, Gibson still owned 30% of the goods. Net income for Sparis was $912,000 during 2018. Assuming there are no excess amortizations associated with the consolidation, and no other intra-entity asset transfers, what was the net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest for 2018
Answers
Answer:
$907,200
Explanation:
Calculation for the net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest for 2018
First step is to calculate the Gross profit rate
Using this formula
Gross profit rate = gross profit + COGS = GPR/ (1-GPR)
Let plug in the formula
Gross profit rate= 25%/(1+25%) = 0.2
intra-entity gross profit = Transfer price x GPR (0.2)
Gross Profit 2017= $84,000 x 30%
Gross Profit 2017= $25,200;
Gross Profit 2018= 100,000 x 30%
Gross Profit 2017= $30,000
Now let calculate 2018 net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest Using this formula
2018 net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest =Subsidiary’s net income + Intra-entity Gross Profit in Ending Inventory for 2017 – Intra-entity grossprofit in 2018 inventory deferred x noncontrolling interest
2018 net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest = ($912,000) + ($25,200) – ($30,000) *10%
= $907,200
Therefore the net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest for 2018 is $907,200
Kally goes to the grocery store each week looking to purchase items that will give her as much utility as possible, given her $100 budget. Last week apples were priced at $4.50 each, and Kally purchased 3 apples. This week apples are on sale for $2.50 each, while all other prices have remained the same, and Kally chooses to purchase 7 apples. Given this information, plot Kally's demand curve for apples.
Answers
Answer:
Please check the attached image for kally's demand curve
Explanation:
The demand curve is a curve that shows the various quantities of a good that is purchased at different prices.
The demand curve is downward sloping due to the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. The higher the price, the lower the quantity demanded and the lower the price, the higher the quantity demanded. This is known as the law of demand.
It can be seen that the quantity demanded of apples increased from 3 to 7 when price reduced to $2.50
On the demand curve, price is on the vertical axis, while quantity demanded is on the horizontal axis
Answer:
Please check the attached image for kally's demand curve
Explanation:
Bauerly Co. owned 70% of the voting common stock of Devin Co. During 2017, Devin made frequent sales of inventory to Bauerly. There was deferred intra-entity gross profit of $40,000 in the beginning inventory and $25,000 of intra-entity gross profit at the end of the year. Devin reported net income of $137,000 for 2017. Bauerly decided to use the equity method to account for the investment. Assuming there are no excess amortizations associated with the consolidation, and no other intra-entity asset transfers, what is the net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest for 2017
Answers
Answer:
$36,600
Explanation:
Calculation for the net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest for 2017
First step is to calculate the Intra-Entity Gain on Transfer That Is Deferred
Intra-Entity Gain on Transfer That Is Deferred=Sales Price $40,000 - BV $25,000 =
Intra-Entity Gain on Transfer That Is Deferred=$15,000
Second step is to calculate the Adjusted Subsidiary Net Income
Adjusted Subsidiary Net Income =Subsidiary's Net Income $ 137,000 - Deferred Intra-Entity Gain on Transfer $15,000
Adjusted Subsidiary Net Income =$122,000
Now let calculate the Noncontrolling Interest in Net Income
Noncontrolling Interest in Net Income = $122,000 × 30% Ownership Interest in Subsidiary
Noncontrolling Interest in Net Income = $36,600
Therefore the net income attributable to the noncontrolling interest for 2017 is $36,600