Answers
Answer:
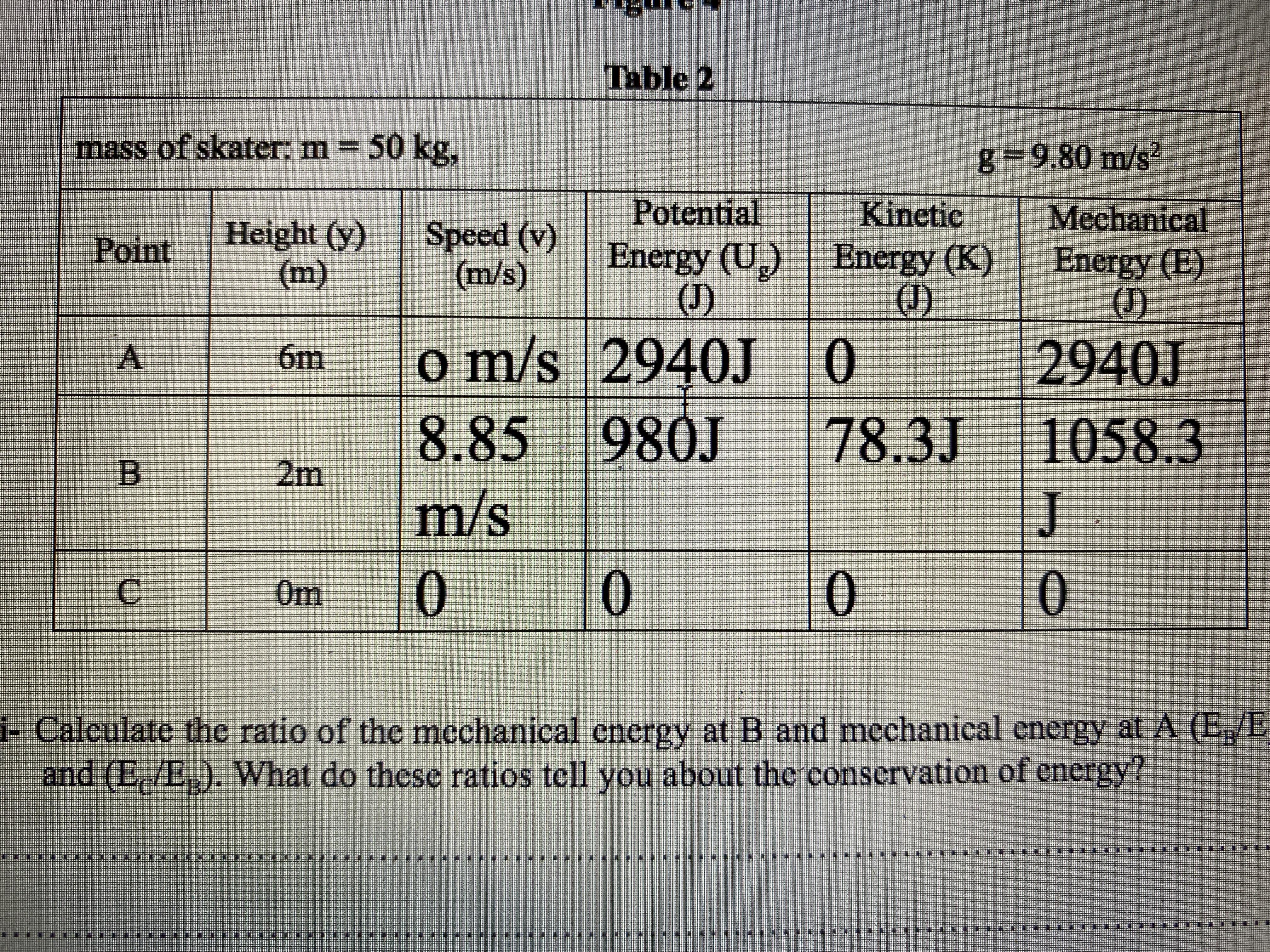
Yes at A the mechanical energy is conserved.
Yes at B the part of mechanical energy is conserved potential energy and kinetic energy and some is lost as frictional force.
Explanation:
Ratio = Eb/ Ea= 1058.3 J/2940 J= 0.3599
Ratio = Ec/ Eb= 0J/ 1058.3 J= 0
At point A the skater is at rest or it is the starting point and the whole energy is due to the position of the skater i.e= mgh = 50 *9.8*6= 2940 J
Since there's no movement there is no Kinetic energy = 0 J
Yes at A the mechanical energy is conserved.
At point B the skater has traveled for some of the distance . It has potential energy and kinetic energy.
Yes at B the part of mechanical energy is conserved as potential energy and kinetic energy.
The total Mechanical energy = 1058.3 J
At point B Total Mechanical energy = PE+ KE
1058.3J = 980 J + 78.3 J
1058.3 J = mgh + 1/2mv²
= 50*2*9.8 + 1/2 *50*(8.85)²
= 980 J + 78.3 J
As the total energy of the system must remain the same some of the mechanical energy is lost as frictional force at point B .
2940 J-1058.3 J= 1881.7
At Point C the skater has arrived at the end point and the height , speed, PE, KE and ME all are zero.
(a) The ratio of the mechanical energy at B and mechanical energy at A is 0.36.
(b) The ratio of the mechanical energy at C and mechanical energy at A is 0.
(c) mechanical energy is conserved between a and b.
(d) mechanical energy is not conserved between b and c.
The given parameters;
mechanical energy at A, [tex]E_a = 2,940 \ J[/tex]mechanical energy at B, [tex]E_b =1,058.3 \ J[/tex]mechanical energy at C, [tex]E_c = 0[/tex]The ratio of the mechanical energy at B and mechanical energy at A;
[tex]ratio = \frac{E_b}{E_a} = \frac{1058.3}{2940} = 0.36[/tex]
The ratio of the mechanical energy at C and mechanical energy at A;
[tex]ratio = \frac{E_c}{E_a} = \frac{0}{2940} = 0[/tex]
The change mechanical energy between A and B from the given position;
[tex]\Delta E = mg(h_b - h_a) - \frac{1}{2}m(v_b^2 - v_a^2)\\\\ \Delta E = 50\times 9.8(2-6) \ - \ \frac{1}{2} \times 50(8.85^2 - 0)\\\\\Delta E =- 1960 + 1960\\\\\Delta E = 0 \ J[/tex]
Thus, we can conclude that mechanical energy is conserved between a and b.
The change mechanical energy between A and B from the given position;
[tex]\Delta E = mg(h_c - h_b) - \frac{1}{2}m(v_c^2 - v_b^2)\\\\ \Delta E = 50\times 9.8(0-2) \ - \ \frac{1}{2} \times 50(0^2 - 8.85^2)\\\\\Delta E = -980 + 1960 \\\\\Delta E = 980 \ J[/tex]
Thus, we can conclude that mechanical energy is not conserved between b and c.
Learn more here:https://brainly.com/question/19969393
Related Questions
What cause objects to move? In three to five sentences .
Answers
Answer:
Gravity can affect the motion of objects as the force pulls objects closer to earth. Kinetic energy also causes movement in objects as that is energy in motion coming from stored energy known as (potential energy). With almost most importantly is needed is a force as without a force acting upon an objects is moving will continue to move and an object at rest will remain at rest as a gravitational pull or kinetic and potential energy for example are forces.
Explanation:
Have a great day :)
Notice that the electromagnet in the virtual simulation is made up of a battery and a wire. What item could you add to the electromagnet to make it even stronger?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Have y’all seen steeleflag19 at all on here?
What is the speaker’s power output if the sound intensity level is 102 dBdB at a distance of 25 mm ? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
Answers
Answer:
Power = 124.50 W
Explanation:
Given that:
The Sound intensity of a speaker output is 102 dB
and the distance r = 25 m
For the intensity of sound,
[tex]\beta (dB)= 10 \ log_{10 } (\dfrac{I}{I_o})[/tex]
where;
the threshold of hearing [tex]I_o = 10^{-12} (W/m^2)[/tex]
[tex]\dfrac{102 }{10}= log_{10}( \dfrac{I}{10^{-12}})[/tex]
[tex]10^{10.2} = \dfrac{I}{10^{-12}}[/tex]
[tex]I = 10^{10.2} \times 10^{-12}[/tex]
I = 0.01585 W/m²
If we recall, we know remember that ;
Power = Intensity × A rea
Power = 0.01585 W/m² × 4 × 3.142 × (25 m)²
Power = 124.50 W
how do you Convert 50 g to kg in an equation for physics
Answers
Answer:
Divide by 1000
Explanation:
An airplane accelerates down a runway at 4.3 m/s2 for 48 s until it finally lifts off the ground. Determine the distance traveled before takeoff.
I
Answers
Answer:
x=4953.6m
Explanation:
used formula x=xo+vot+1/2at^2
An airplane, starting at rest, takes off on a 600. m long runway accelerating at a rate of 12 m/s/s. How many seconds does it take to reach the end of the runway?
Answers
Answer:
10 seconds
Explanation:
As it starts from rest, then u=0
and by III rd equation of motion:
A ray is incident at at 50 degrees angle on a plane mirror. What will be the deviation after reflection from the mirror?
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
If the ray were not deviated, it would travel straight through the mirror. Due to the mirror, the incident ray is reflected at 30°. The ray travels 30° + 30° = 60°. The angle of deviation is 180° - 60° = 120°.
100 POINTS.
Please provide explanation.
Thank you
Answers
Answer:
(a) 0.829 m/s
(b) 3.27 m/s
(c) 0.000153 m²
55.8%
Explanation:
(a) Flow rate equals velocity times cross-sectional area. (1 L = 0.001 m³)
Q = vA
(0.001 m³ / 2.00 s) = v (48 × π (0.002 m)²)
v = 0.829 m/s
(b) Use Bernoulli equation. Choose point 1 to be the exit of the pump, and point 2 to be exit of the shower head. Choose 0 elevation to be at point 1.
P₁ + ½ ρ v₁² + ρgh₁ = P₂ + ½ ρ v₂² + ρgh₂
(1.50 atm × 1.0×10⁵ Pa/atm) + ½ (1000 kg/m³) v² + 0 = (1 atm × 1.0×10⁵ Pa/atm) + ½ (1000 kg/m³) (0.829 m/s)² + (1000 kg/m³) (10 m/s²) (5.50 m)
1.50×10⁵ Pa + (500 kg/m³) v² = 1×10⁵ Pa + 414.5 Pa + 55000 Pa
v = 3.27 m/s
(c) Flow rate is constant.
Q = vA
(0.001 m³ / 2.00 s) = (3.27 m/s) A
A = 0.000153 m²
Flow rate is proportional to the pressure difference and the radius raised to the fourth power.
Q ∝ ΔP r⁴
Q₂/Q₁ = (ΔP₂/ΔP₁) (r₂/r₁)⁴
Q₂/Q₁ = (1.120) (0.840)⁴
Q₂/Q₁ = 0.558
The flow decreases to 55.8% of the original value.
Answer:
Explanation:
Regarding the point of "Flow rate is proportional to the pressure difference and the radius raised to the fourth power", flow rate depends on pressure, cross-section area and speed. As speed also depends on cross-section area, flow rate becomes dependent on pressure and cross-section area squared.
In a round pipe like blood vessel, the cross-section area is equal to pi*radius squared. So flow rate is proportional to the pressure difference and (radius squared) squared; i.e. the radius raised to the fourth power.
The new flow rate = (1.12)*(0.84)^4
=0.5576 or 55.76% of the original flow rate
The acceleration of the spacecraft in which the Apollo astronauts took off from the moon was 3.4 m/s2 m / s 2 . On the moon, g g = 1.6 m/s2 m / s 2 . what's the apparent weight
Answers
Complete Question
The acceleration of the spacecraft in which the Apollo astronauts took off from the moon was 3.4 m/s2. On the moon, g = 1.6 m/s2. What was the apparent weight of a 75 kg astronaut during takeoff?
Answer:
The value is [tex]N = 375 \ N[/tex]
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The acceleration is [tex]a = 3.4 \ m/s^2[/tex]
The acceleration due to gravity in the moon is [tex]g = 1.6 m/s^2[/tex]
The mass of the astronaut is [tex]m = 75 \ kg[/tex]
Generally the apparent weight is mathematically represented as
[tex]W = ma + mg[/tex]
=> [tex]W = 3.4 * 75 + 1.6 * 75[/tex]
=> [tex]W = 375 \ N[/tex]
A 30.0-kgkg box is being pulled across a carpeted floor by a horizontal force of 230 NN , against a friction force of 210 NN . What is the acceleration of the box?
Answers
Answer:
The acceleration of the box is 0.67 m/s²
Explanation:
Given that,
Mass of box = 30.0 kg
Horizontal force = 230 N
Friction force = 210 N
We need to calculate the acceleration of the box
Using balance equation
[tex]F-f_{k}=ma[/tex]
[tex]a=\dfrac{F-f_{k}}{m}[/tex]
Where, F = horizontal force
[tex]f_{k}[/tex] =frictional force
m= mass of box
a = acceleration
Put the value into the formula
[tex]a=\dfrac{230-210}{30}[/tex]
[tex]a=0.67\ m/s^2[/tex]
Hence, The acceleration of the box is 0.67 m/s²
Please help
A student plans an investigation to determine the refractive index of glass. The student uses this equipments.
- a ray box
- a rectangular glass block
- a protractor
- a pencil
Describe how the student collect her data.
Answers
Calculate the effective charges on the H and F atoms of the HF molecule in units of the electronic charge, e.
Answers
Answer:
Explanation:
Hydrogen fluoride (HF) is an ionic/electrovalent compound that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water. It's dissociation is as seen below
HF ⇄ H⁺ + F⁻
There is a transfer of electron from the hydrogen atom which produces the hydrogen ion (H⁺), while the fluorine atom receives the donated ion to become negatively charged (F⁻). The amount of charge in one electron is generally given as 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ coloumbs.
The required value of effective charge on HF molecule, due to H and F is 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ Coulombs.
The given problem is based on the concept of effective charges. The net positive charge carried out by the electrons of atomic species, after forming a polyelectronic atom is known as Effective charge.
As per the given problem, the Hydrogen fluoride (HF) is an ionic/electrovalent compound that dissociates into ions when dissolved in water. It's dissociation is given as,
HF ⇄ H⁺ + F⁻
There is a transfer of electron from the hydrogen atom which produces the hydrogen ion (H⁺), while the fluorine atom receives the donated ion to become negatively charged (F⁻). The amount of charge in one electron is generally given as 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ Coulombs.
Thus, we can conclude that the required value of effective charge on HF molecule, due to H and F is 1.602 × 10⁻¹⁹ Coulombs.
Learn more about the effective charge here:
https://brainly.com/question/25002720
What measurements would you make (assuming you have the money, time, & equipment) to determine a star’s surface temperature? Explain your answer.
Answers
Answer:
use special filters on the telescope
Explanation:
Assuming you have access to a very high-grade telescope you would need to use special filters on the telescope that allows you to view the star's color spectrum. The color spectrum represents different levels of heat that a star is generating. This spectrum ranges from red to blue. Therefore in order to calculate the surface temperature, you would need to apply both a blue and red filter onto the telescope. Once you have these measurements you would need to compare them in order to pinpoint the correct variation of color which would give a close enough estimate of the surface temperature of the star.
How do I proton and and electron compared
Answers
A 0.5 kg basketball moving 5 m/s to the right collides with a 0.05 kg tennis
ball moving 30 m/s to the left. After the collision, the tennis ball is moving 34
m/s to the right. What is the velocity of the basketball after the collision?
Assume an elastic collision occurred.
O A. 11.4 m/s to the left
O B. 11.4 m/s to the right
O C. 1.4 m/s to the right
O D. 1.4 m/s to the left
Answers
Answer:
1.4 m/s to the left
Explanation:
just took it c:
3 For this force system the equivalent system at P is ___________ A FRP 40 lb along x dir and MRP 60 ft lbB FRP 0 lb and MRP 30 ft lbC FRP 30 lb along y dir and MRP 30 ft lbS FRP 40 lb along x dir and MRP 30 ft lb
Answers
This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
For this force system the equivalent system at P is ___________
A) FRP = 40 lb (along +x-dir.) and MRP = +60 ft.lb
B) FRP = 0 lb and MRP = +30 ft.lb
C) FRP 30 lb (along +y-dir.) and MRP = -30 ft.lb
D) FRP 40 lb (along +x-dir.) and MRP = +30 ft.lb
Answer:
D) FRP 40 lb (along +x-dir.) and MRP = +30 ft.lb
Explanation:
From the figure in the image i uploaded along this answer;
FRP = ( 40 lb i + 30 lb j ) + [30 lb (-j)]
Where i and j are the unit vectors along X & Y axis respectively.
So, FRP = 40 lb i
that is, FRP = 40 lb along +X direction
MRP = [ 30 lb x ( 1 ' + 1' ) ] +( -30 lb x 1 ' )
= (30 lb x 2 ' )- 30 lb ft
= 60 lb ft - 30 lb ft
= 30 lb ft
Therefore option(D) is correct
waht is science
wjwissbsskdldmndndnd
Answers
Answer:
the intellectual and practical activity encompassing the systematic study of the structure and behaviour of the physical and natural world through observation and experiment.
Explanation:
Which best explains a difference between Einstein’s general theory of relativity and his special theory of relativity?
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to uniform motion.
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to accelerated motion.
His general theory applies only to accelerated motion, but his special theory includes uniform and accelerated motion.
His general theory applies only to uniform motion, but his special theory includes uniform and accelerated motion.
Answers
Answer:
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to uniform motion.
Explanation:
According to Einstein's 1915 general theory of relativity, the force of gravity arises from the curvature of space and time.
According to theory of special relativity:
1. The laws of physics are the same for all non-accelerating observers
2. The speed of light in a vacuum was independent of the motion of all observers.
His general theory includes uniform and accelerated motion, but his special theory applies only to uniform motion.
Answer:
for those who dont like to read
the answer is A.
hope i helped
Explanation:
On what part of the eye are rods and cones found?
Answers
Answer:
retina.
Explanation:
A car moving with an intial velocity of 60m/s is brought to rest in 30 seconds calculate the acceleration
Answers
Answer:
a = 2 [m/s^2]
Explanation:
To solve this problem we must use the expressions of kinematics, we must bear in mind that when a body is at rest its velocity is zero.
[tex]v_{f} = v_{i} - (a*t)[/tex]
where:
Vf = final velocity = 0
Vi = initial velocity = 60 [m/s]
a = desacceleration [m/s^2]
t = time = 30 [s]
Note: the negative sign of the above equation means that the car is slowing down, i.e. its speed decreases.
0 = 60 - (a*30)
a = 2 [m/s^2]
Please provide explanation!!!
Thank you.
Answers
Answer:
(a) 102 cm/s
(b) 0.490 cm²
Explanation:
(a) Use Bernoulli equation.
P₁ + ½ ρ v₁² + ρgh₁ = P₂ + ½ ρ v₂² + ρgh₂
0 + ½ ρ v₁² + ρgh₁ = 0 + ½ ρ v₂² + 0
½ ρ v₁² + ρgh₁ = ½ ρ v₂²
½ v₁² + gh₁ = ½ v₂²
½ (25.0 cm/s)² + (980 cm/s²) (5.00 cm) = ½ v²
v = 102 cm/s
(b) The flow rate is constant.
v₁ A₁ = v₂ A₂
(25.0 cm/s) (2.00 cm²) = (102 cm/s) A
A = 0.490 cm²
A solid nonconducting sphere of radius R carries a charge Q distributed uniformly throughout its volume. At a certain distance rl (r
(A) E/8
(B) E 78.
(C) E/2
(D) 2E
(E) 8E
Answers
Answer:
A ) E/8
Explanation:
If the sphere of radius R carries charge Q, then the volumetric charge density is:
ρ₁ = [Q/ (4/3)*π*R³]
Therefore the net charge inside r ( r < R ) is:
q₁ = ρ * (4/3)*π*r³
And E = K * q₁/r K = 9,98 *10⁹ [N*m²/C²]
E = K * ρ * (4/3)*π*r³/r
E = K * ρ * (4/3)*π*r²
If now the charge is distributed over a sphere of radius 2R
ρ₂ = [Q/ (4/3)*π*(2R)³]
ρ₂ = [Q/ (4/3)*π*8*R³]
Then ρ₂ < ρ₁ in fact ρ₂ = (1/8)*ρ₁
The electric field depends on the net charge enclosed by a gaussian surface, and the distance between the net charge and the considered point, ( considering the net charge as being at the center of the gaussian surface) In this case, there was no distance change then
E₂ = E₁/8
The right answer is lyrics A ) E/8
I WILL MARK YOU AS BRAINLIEST IF RIGHT
What is the magnitude of the net force acting on this object?
Answers
Answer:
The net force on an object is the total force applied on the object after adding up all the forces
In the given diagram,
we can see that the 2 forces of 4N and 4N will cancel each other out since they are equal and in the opposite direction
Now, we are left with a force of 2N and 10N,
the net force will be the difference of these forces:
Net force = 10N - 2N
Net force = 8N downwards
Another way to do it:
The two 4N forces will be cancelled out,
and we are left with a 2N and a 10N force
(notice how we cancelled equal and opposite forces for the 4N)
We can divide the 10N force into (2N + 8N)
Since the 2N forces are equal and opposite, they will be cancelled out
and we will be left with a net force of 8N downwards
Matching type. Send help please. ASAP!
Answers
Answer:
46-D
47-C
48-F
49-A
50-B
I am not very sure I am right about those answers though.
(iii) Why do right angle mirrors produce three images of the object?
Answers
Explanation:
The two mirrors inclined to each other formed the first two images with are of the same size as the object while the third mirror is produced from the intersection of rays that emanated during the production of the first two images to produce a third image which is smaller than the object and there making the total number of images to be 3.
Hence this mirrors produces 3 images due to the third image formed from the intersection of the rays that produces the first two images.
The formula that relates the image produced by inclined mirror and the angle of inclination is expressed as:
number of images n = 360/θ - 1
θ is the angle of inclination of the two mirrors
n is the number of images
If the mirrors are inclined at right angles, then θ = 90°
Substitute into the formula;
n = 360/90 -1
n = 36/9 -1
n = 4-1
n = 3
Determine the electrical force of attraction between two balloons
that are charged with the opposite type of charge but the same
quantity of charge. The charge on the balloons is 6.0 x 10-7 C and they
are separated by a distance of 0.50 m.
Answers
Answer:
F=1.3x10^-2N
Explanation:
Fe= k(6x10^-7C)^2/(0.5)^2
Electrical force of attraction between the balloons is F=1.3x10^-2N
The electric force of attraction between two balloons should be F=1.3x10^-2N.
Calculation of the electric force;Since The charge on the balloons is 6.0 x 10-7 C and they are separated by a distance of 0.50 m.
So, here the electric force is
Fe= k(6x10^-7C)^2/(0.5)^2
F=1.3x10^-2N
hence, The electric force of attraction between two balloons should be F=1.3x10^-2N.
Learn more about force here: https://brainly.com/question/19848845
A force of 15 newtons is used to push a box along the floor a distance of 3 meters. How much work was done?
Answers
Answer:
The answer is 45 JExplanation:
The work done by an object can be found by using the formula
workdone = force × distanceFrom the question
distance = 3 meters
force = 15 newtons
We have
workdone = 15 × 3
We have the final answer as
45 JHope this helps you
how are s waves and p waves simuliar?
A.they shake the ground
B.they travel through liquids
C. they arrive at the same time
D.they shake the ground from side to side
Answers
Answer:
A
Explanation:
hope this helps
Six seconds after starting from rest, a car is moving at 15 m/s. What is the car's
average acceleration?
6 m/s2
0-5 m/s?
5 m/s2
2.5 m/s?
-2.5 m/s?
Answers
Answer:
2.5 m/s²
Explanation:
a = ∆v/∆t = (15 m/s)/(6 s) = (15/6) m/s² = 2.5 m/s²
Who was the first who traveled to the moon?
Answers
NEIL ARMSTRONG WAS THE FIRST MAN WHO TRAVELLED TO THE MOON.
Answer:
On July 20, 1969, Neil Armstrong became the first human to step on the moon.